Brain Damage Biomechanics from Traumatic Forces
Brain Damage Biomechanics
Call me at 800-992-9447
Mechanisms of Brain Injury Neuropathology
In examining brain damage biomechanics, it is not the blow or the whiplash, but what happens inside the skull, which causes the injury. The two most significant causes of brain injury are the “contact” of the head with a blunt object and the “inertia” as a result of a rapid acceleration or deceleration of the brain. The terms “impact” and “shear” are also often used to differentiate the internal mechanisms of injury between the contact and inertial sources of injury for Brain Damage Biomechanics. The term “contact phenomenon” is used to describe what occurs when the energy of the impact of the head with something is transferred to the brain.
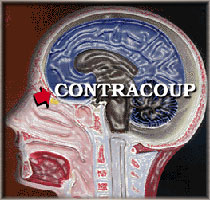
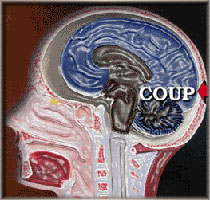
Coup – Contracoup Brain Injury
Injury from contact phenomenon can occur at more than the site of the initial impact of the brain with the skull. Contact phenomenon brain injury can also happen because of the rebound of the brain from the initial impact inside the skull. To describe this phenomenon, the terms coup and contra coup (rebound) are used.
The Biomechanical model of the coup, contracoup is more valuable as a teaching tool than a road map to find the precise pathology. While the brain does in fact bounce inside the skull after a contact force, the site most often to be injured by the contracoup impact is not the opposite side of the brain, but the underside of frontal lobes and temporal lobes.
These next three graphics were developed to illustrate the vectors of force inside the brain involved in an impact mechanism.

Brain Damage Biomechanics of the internal rebound of the brain in the contracoup mechanism is shown here.
More complex Brain Damage Biomechanics are beyond the mission of BrainInjuryHelp.com We will discuss more specifics about the “rotational” force in our treatment of Mild Brain Injury Neuropathology here.
For Brain Injury Care and Rehabilitation, click here.
For Brain Injury Symptoms, click here.
To return to our main page, click here.